INTRODUCTION
Global enterprises are facing unprecedented challenges posed by market disruption from digital native firms as well as unparalleled opportunities unleashed by the convergence of emerging technologies and innovative business models. Navigating through this vortex requires significant innovation and re-invention of the enterprise. Organizations need the support of an ecosystem of partners – technology vendors, service providers and advisors to successfully execute upon digital transformation.
Progressive enterprises recognize that digital transformation at scale can only be effectively executed by partnering with truly visionary service providers. Identifying the right partner for a company’s transformational programs, that is, a partner that enables hyper-convergence of technology prerequisites, is a critical factor in ensuring digital success.
The digital disruption is unfolding faster than any of the other earlier economic revolutions
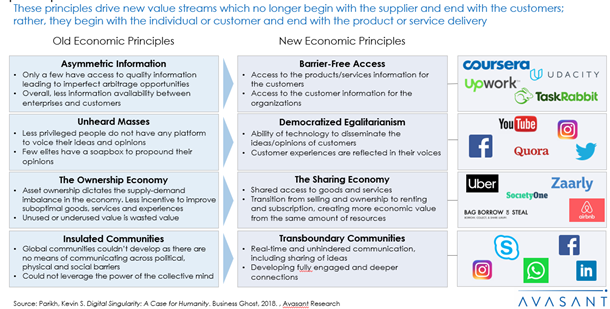
The digital disruption we are experiencing now is unfolding faster than any of the other earlier economic revolutions. The technological advancements fuelling this disruption has fundamentally changed the principles on which all economic activity used to occur. The new economy that is evolving in front of us is one where individuals experience barrier-free access, democratized egalitarianism, sharing economy and transboundary communities. The new economy has empowered the consumer into a digital being and has brought new companies into play thus changing the traditional competitive landscape.
Technology has changed the fundamental economic principles
In the face of this accelerated disruption, enterprises need to acknowledge and adapt to these technology-led changes to remain relevant and competitive. The true digital transformation journey of enterprises requires having a robust and radical business-driven technology strategy, with initiatives spanning multiple emerging technologies. However, a key constraint in execution of this strategy is the limited in-house availability of skills, resources and expertise.
And that is where the increased need for deep partnerships with service providers and other ecosystem players becomes critical for progressive enterprises. The biggest challenge is that digital transformation requires provider partners to have service capabilities that are very different from more traditional technology-centric services. Enterprises have been assessing service providers around traditional services and have built comprehensive methodologies to choose the right provider to partner with. However, assessing digital providers requires a new and innovative framework that essentially measures new age dimensions that are most critical to evaluating them as long-term partners for digitally evolving global organizations.
Avasant’s RadarViewTM Methodology
Avasant’s RadarViewTM methodology distills down to three critical dimensions and helps reflect the true digital capabilities of service providers:
- Practice Maturity: This dimension considers the maturity of their offerings and capabilities in emerging technologies, the nature and sophistication of solutions, use cases addressed, quality of talent and execution capabilities
- Investments and Innovation: This dimension assesses how their investment approach and innovation focus align with the future direction of the industry
- Industry Development: This dimension focuses on provider’s initiatives towards market creation and development, knowledge development and collaboration with industry stakeholders
However, to derive true business value from digital transformation programs, another important element that enterprises should focus on is to identify partners that can converge multiple emerging technologies as part of a broader business strategy. These partners need to have the ability to move the enterprises on the digital maturity ladder and achieve digital singularity where enterprise’s business and digital strategies align with each other. Zeroing in on such partners also requires evaluation criterion that assesses the provider’s capability not only for specific technology but also how it seamlessly integrates multiple technologies together for true digital transformation:
Such providers can be called Digital Masters as they bring together three key areas:
- Digital Prerequisites: This dimension considers provider’s capabilities in individual digital technologies, the maturity in these capabilities and how are they building these capabilities
- Digital Convergence: This dimension considers provider’s approach and experience with implementing projects that leverage multiple technologies together within a holistic transformation framework
- Future Centricity: This dimension considers their approach and strategy for staying ahead of their digital curve, their investments in digital tools, solutions, platforms, IP development and engagement with cutting edge technology companies
Convergence of multiple technologies has the ability to accelerate enterprises’ ability to generate new opportunities. For instance, although IoT can facilitate the digitization of the information itself, the reliability and security of such information is still a key challenge. Blockchain can help in addressing major security requirements and solve challenges such as immutability, transparency, auditability, data encryption and operational resilience. In January 2018, IBM and global shipping leader Maersk announced an initiative to create a global trade platform on Blockchain, TradeLens, that enables multiple trading partners to collaborate by establishing single shared view of a transaction without compromising details, privacy or confidentiality. These parties can interact more efficiently through real-time access to shipping data and shipping documents, including IoT and sensor data ranging from temperature control to container weight. TradeLens has already logged more than 230 million shipping events and is set to process more than 20 million containers.
Similarly, when other technologies such as artificial intelligence and RPA integrate, they create the ‘smart’ feature. Machine learning lets robots learn how to process and automate the emotional- and judgement- based processes. Hollard Group, a privately-owned insurance group in South Africa has integrated AI services for end-to-end automation to access and interpret 1.5 million emails and their attachments every year to handle each insurance claim. These robots also interact with human employees to execute instructions and deliver completion confirmations. This has resulted in 600% faster claim processing and 91% lower cost per transaction.
Avasant Digital Masters RadarViewTM 2019
Avasant Digital Masters RadarViewTM 2019 has identified 16 such partners whose focus is on building capabilities that cater to enterprises’ current and future needs enabling them to achieve this digital convergence. The featured providers, or ‘Digital Masters’ exemplify the ability to drive such engagements that leverage multiple technologies together. To enable enterprises achieve this digital convergence, Digital Masters have already started evolving their portfolio of digital offerings. They have put significant focus on improving their digital capabilities through both organic and inorganic approaches. They have used acquisitions as an effective strategy to build future capabilities with speed and scale across areas such as big data and analytics, design capabilities, digital consulting, product engineering, IoT, cloud capabilities, etc.
Approximately 2.1 times more such acquisitions have been done by Digital Masters than other service providers. In addition to these investments, they are putting significant investments to drive innovations by incubating and investing in emerging technology start-ups. Since 2014, the start-up investments to create innovative enterprise technologies by Digital Masters is twice of those by other providers. By putting their clients at the center, Digital Masters are continually innovating with their client engagement models by investing in design thinking firms. 14 acquisitions of design-thinking firms have been done across all Digital Masters to strengthen their design capabilities. To bring digital mindset throughout their organization, they are bringing digital expertise in their board room.
Undoubtedly, today enterprises need to understand that failure to respond and embrace changes led by digital technologies will make them irrelevant in the marketplace. But, by being open to and leveraging the wide partnership ecosystem, they can achieve the status of a true digital enterprise.
The rules of the new economy are fundamentally changing the business landscape. Barrier-free Access gives us direct access to compete in the global, digital economy and gives rise to the gig economy. Democratized Egalitarianism, the ability of technology to further the equality of all voices, breaks down the walls between individuals and CEOs, challenging businesses to act differently. The Sharing Economy involving collaborative sharing of talents, products and services, and non-traditional employment is on the rise. And Transboundary Communities provide new types of places where individuals decide how to allocate their time and talents to earn a living, work with others, compete and start new businesses.
As we move towards Digital Singularity, organizations are frantically putting together a strategy which will enable them to thrive in the new digital economy. Digital has become the new status quo, with technology leveling the playing field. Business cycles are shortening. Barriers to entry are increasingly declining, with many large, traditional organizations being disrupted by smaller, tech-savvy start-ups. The business ecosystem now operates in a ‘Switching Economy,’ with competition like never before. Executives are continuously challenged. Are their competitive differentiators, truly competitive? How do they ensure they stay ahead of the curve? How do they minimize risk of being disrupted?
To remain relevant companies must forge creativity and continuously innovate. Enterprise Disruption is the technological disruptions across business models and value chains, driven by innovation, to fundamentally transform how businesses operate and remain competitive. Innovation lies at the core of truly disruptive enterprises, with many of the world’s leading companies not just embracing innovation, but actively and aggressively institutionalizing innovation within their organizations, and constantly challenging the status quo. Amazon, Google, Apple, Uber and Netflix are just some examples of disruptive enterprises which have mobilized innovation and integrated technology to not only transform business models, but the entire consumer experience and expectations. This has set a new precedent for the way we operate and engage in the digital economy.
Download this article as a whitepaper.
Related: Hyper-Sustainability: A Guide to 10X Transformation
Related: Artificial Intelligence: Driving the Evolution of the New-Age Talent Market
Related: The Digital Transformation Journey: Lessons from a CIO's Perspective
Related: Building the Digital Enterprise
