The Journey Toward Intelligent Automation
Defined as the application of robotic process automation (RPA) along with artificial intelligence (AI) and technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing and computer vision, Intelligent Automation (IA) is bringing fundamental changes to how enterprises operate. Both the work (i.e., business processes) and the worker (i.e., resources) are evolving at breakneck speeds. The workforce now includes machines with software intelligence that enable enterprises to handle unstructured data rapidly, achieve savings within 6-9 months, 100% ROI by the second year, and above 90% efficiency gains. Beyond these hard business benefits, IA brings new skills that enable people to develop entirely new processes, essentially carving out new directions to expand what’s possible for their enterprises.
RPA Has Come A Long Way
RPA, the earliest form of IA, has significantly matured over the last four to five years. According to Avasant’s RadarViewTM, 2018 is the year when Global 2000 organizations across industries will embrace it for multi-process use cases and achieve large-scale benefits. The demand for RPA is driven by business objectives of achieving better compliance, quicker cycle time and autonomous processing. By this year, 40% of RPA adopters would have moved beyond experimentation to early adoption of AI to drive business process transformation. A combination of cognitive technologies is being increasingly utilized by industries such as banking, insurance, finance and retail to deliver more value in front-, mid- and back-office processes.
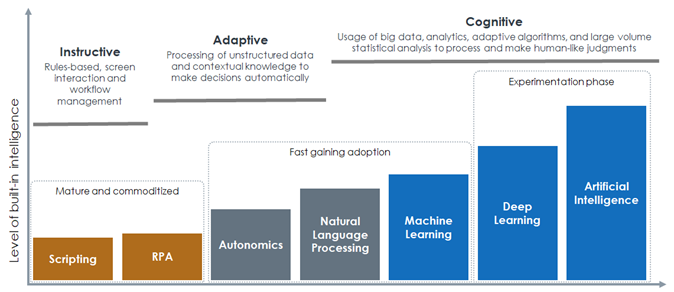
Several enterprises see the adoption of intelligent automation as a journey towards progressive adoption of cognitive technologies:
Pitfalls in the Journey
Despite the purported ease of implementation of IA, several engagements do not achieve the returns that enterprises expect. These are the common pitfalls enterprises encounter when trying to scale IA:
- Moving to scale without a defined automation program
- Choosing the wrong processes
- Lack of a strong business case
- Lack of early engagement with key stakeholders
- Lack of a change management program
- Selecting the wrong tool and implementation partner
Access the full article for further insights into the journey to intelligent automation, including a detailed discussion of the points above and more.
Download the full Intelligent Automation Services RadarViewTM Report 2018 to learn more about the Intelligent Automation Service landscape.
Related: 7 Levels of RPA Adoption
Related: Common RPA Implementation Challenges
Related: 4 Stages of Intelligent Automation Maturity
